The multiple body system
represents a special category of diseases which contains a number of disorders.
These impairments would not fit into any of the
other medical systems.
This system contains
some very unusual diseases like leprosy, but we will concentrate on those disorders you
are more likely to encounter.
General
Evaluation
The term multiple body is used
to illustrate the fact that disorders of this category often affect one or more other body
systems.
When evaluating impairments of this
system, keep in mind that the disease alone may not in and of itself be a disabling
impairment.
However, the disease may have a
destructive effect on other organs.
These
disorders may induce enough physical or mental restrictions to preclude work.
The following is a list of the most commonly seen
disorders of the multiple body system.
We
will discuss these disorders as to their common effects on other body systems, as well as
some of the commonly seen supportive evidence.
Systemic Lupus
Erythematosis
Immune related disorders (AIDS), etc.
Obesity
Systemic Lupus
Erythematosus:
Lupus is an inflammatory
disorder of unknown etiology (cause).
Its
common early symptoms are fever, joint pain, and a reddish skin rash appearing on the
face, neck, chest or back.
Lupus is a
progressive disorder which can cause joint deformity, extreme pain and decreased range of
motion of the involved joints. Recurrent
lung and heart infections are also commonly seen in lupus sufferers.
A claimant with lupus may
experience central nervous system involvement causing personality changes, epileptic
seizures, memory problems and psychosis.
The kidneys can also be affected which
can lead to extensive kidney damage and death.
As
you can see, lupus can affect a number of organ systems and should be evaluated as to its
effects on those systems.
Do not hesitate to argue for a
decreased physical or mental RFC if your claimant is showing dysfunction of any type due
to this impairment.
Obesity:
Obesity is a serious disorder
although many would argue that it is self-induced.
This
may be the case, but how it occurred is irrelevant to the fact that it exists and the
claimant is suffering from it.
When evaluating an obese
individual, note complaints of joint pain, inability to stand and walk, decreased mobility
of the body in general and hypertension.
The
obese individual may also have problems with heart disease, lung disease and circulatory
problems in the legs.
Any of the above
symptoms can significantly reduce a very obese person's ability to perform physical
activity.
Obesity causes the heart to work
much harder to do simple activity, causing easy fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath,
and more.
All of the above can be used to
argue for a reduced RFC in the obese person.
The most commonly suffered
disorder in the obese individual is arthritis of a major weight bearing joint.
Major weight bearing joints include the hips,
knees and ankles and spine.
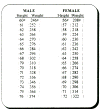
SSA has a weight
scale which is slightly different from the scale given in this chapter.
You will most often handle cases of claimants who
did
not meet
the SSA listing
scale, but still are suffering
from highly restrictive disorders.
If the
claimant is close to our weight scale below and has evidence of arthritis in any weight
bearing joint, you should significantly reduce the claimant's RFC.
The strongest supportive
evidence of arthritis of a weight bearing joint are x-rays, decreased ROM, swelling,
stiffness and pain.
The medical evidence will
supply this and other symptoms from physical exams.
The following is a scale of heights
and weights in both males and females.
If a
person is within 15 pounds of the given weight below for his/her height and is suffering
from any of the problems mentioned earlier, you can win the case.